Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we think about data management and security. Initially developed as the backbone for Bitcoin, its applications have expanded far beyond cryptocurrency. This article will break down the key concepts of blockchain technology and explain why it matters.
What is Blockchain?
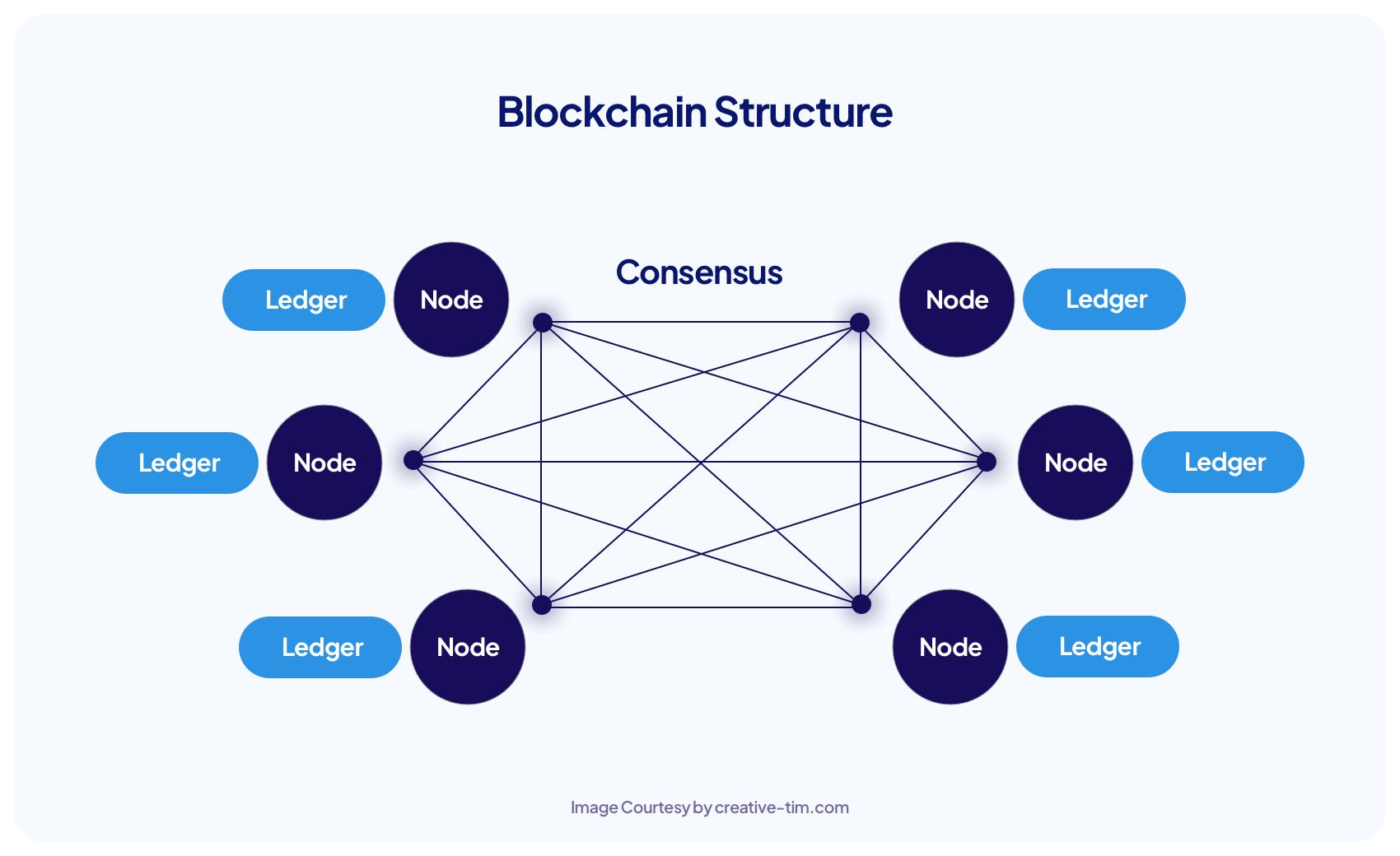
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. This technology ensures that the recorded transactions are secure, transparent, and immutable. Each block in the chain contains a list of transactions and is linked to the previous block, forming a continuous chain.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain operates through a network of computers (nodes) that validate and record transactions. Here’s how it works:
- Transaction Initiation: A user initiates a transaction, which is broadcasted to the network.
- Verification: Nodes in the network verify the transaction through consensus mechanisms.
- Block Creation: Verified transactions are grouped into a block.
- Chain Addition: The new block is added to the existing blockchain.
- Completion: The transaction is complete and can’t be altered.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is defined by several key features:
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases controlled by a single entity, blockchains are distributed across many nodes.
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to anyone with access to the blockchain.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be changed or deleted.
- Security: Cryptographic techniques protect data integrity and user anonymity.

Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms are essential to maintaining the integrity of a blockchain. They ensure that all nodes agree on the validity of transactions. The most common consensus mechanisms include:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions (used by Bitcoin).
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to "stake" as collateral.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Stakeholders elect a small number of delegates to validate transactions on their behalf.
Types of Blockchain
There are several types of blockchains, each serving different purposes:
- Public Blockchain: Open to anyone; everyone can participate (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum).
- Private Blockchain: Restricted access; controlled by a single organization.
- Consortium Blockchain: Controlled by a group of organizations; suitable for collaborative projects.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain has a wide range of applications across various industries, including:
- Finance: Cross-border payments, remittances, and smart contracts.
- Supply Chain: Tracking goods from origin to destination for transparency and accountability.
- Healthcare: Secure sharing of patient records among authorized parties.
- Voting Systems: Ensuring transparent and tamper-proof elections.

Challenges of Blockchain Technology
Despite its potential, blockchain faces several challenges:
- Scalability: As the number of transactions increases, blockchains can become congested.
- Energy Consumption: PoW mechanisms require significant computational power, leading to high energy use.
- Regulatory Issues: Uncertain regulations can hinder widespread adoption.
Future of Blockchain Technology
The future of blockchain technology looks promising. As more industries explore its benefits, we can expect innovations in scalability, security, and user experience. Decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are just the beginning.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is poised to transform various sectors by enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency. Understanding its key concepts will empower individuals and organizations to leverage its potential in the digital age.
